Technical Information
QEEG Procedure and Equipment
The QEEG is acquired in the following manner:
o The subject is comfortably seated and still in an armchair in a quiet setting
o An electro-cap featuring the standard 10-20 international system of electrode arrangement is positioned on the head with two (A1/A2) ear references
o Background interference should be negligible
o Recording equipment should be in sound working order
o Resting State EEG (Predominantly neuronal electrical activity) is recorded for 5 minutes in both eyes open (EO) and eyes closed (EC) conditions
o The QEEG is captured on a Mitsar-EEG-201BT system with 21 EEG and 8 POLY channel amplifier and Win-EEG software
o Impedances on all electrode sites are kept under 5u Ohms for the duration of the recording and retested between conditions
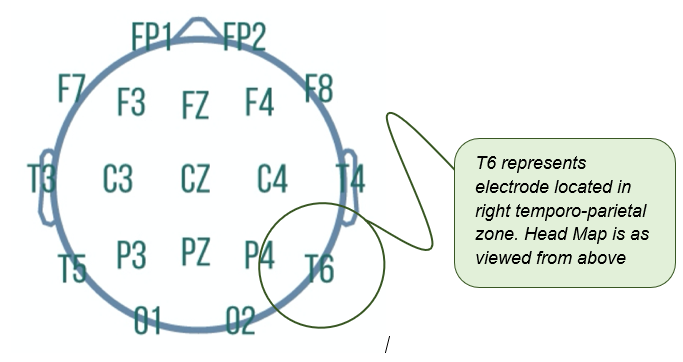
Electrode Configuration
The International 10-20 system of electrode placement is as displayed below.
Electrode sites represent general brain regions and are labelled as follows:
o Frontal (F)
o Temporal (T)
o Parietal (P)
o Occipital (0)
The qEEG captures 0.3-70 hertz frequencies at a sampling rate of 250 Hertz

QEEG Analysis
The assessment process used for reports consists of obtaining the raw recorded EEG, which is then refined by various complex algorithms and advanced software in the following manner:
o Mathematical models are used to generate a series of spectra and maps which represent the neuronal and other electrical activity as measured in brain regions at the time of the assessment
o For simplification and analytical purposes, the Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT) converts the raw EEG into a frequency spectrum (0.5-30 hertz range). FFT expresses the digital recording in time versus frequency format. Waveforms are commonly understood and studied in terms of frequency bands, namely Delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta and Gamma
o QEEG data is improved by identifying and removing waveforms related to eye movements (eg blinking) and muscle activity (eg swallowing/moving). WinEEG Independent Component Analysis (ICA) and Manual Artefact Rejection programs are sometimes utilized for spectra and mapping production. In addition to the manual removal of artefacts, Neuroguides Automatic Rejection program aids in the correction of the EEG for the LORETA 3D Neuro Navigator model
o Several QEEG montages (Bipolar, Reference, Average and Laplacian) are employed to examine the nature and polarity of the waveforms
o Spectra and maps including power and amplitude, asymmetry and coherence, Theta-Beta and other relative power comparisons are generated from the artefact free, modified EEG in Win-EEG and Neuroguide software programs
o Z score results are formulated from comparisons to the Neuroguide normative database which comprises 678 healthy subjects. Further database details can be obtained from www.appliedneuroscience.com
o Client symptoms and personal data are correlated with results of the QEEG, identifying atypical brain patterns to devise a suitable treatment plan